-

-
A Study on the Nondestructive Method for Estimating the Compressive Strength of Materials
재료의 비파괴 압축강도 산정방법에 관한 연구
-
Moorak Son, Jinhyun Seong
손무락, 성진현
- This study aims to propose a non-destructive method for evaluating the compressive strength of materials such as rock and concrete. Rather than …
본 연구는 암석 및 콘크리트와 같은 재료의 압축강도를 비파괴적으로 평가하기 위한 방법을 제안하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 단일 타격에 국한하지 않고, …
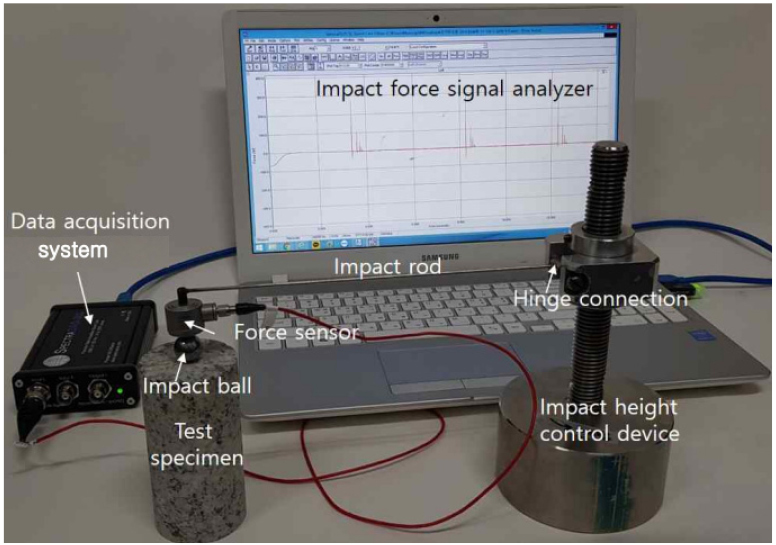
- This study aims to propose a non-destructive method for evaluating the compressive strength of materials such as rock and concrete. Rather than being limited to a single impact, the proposed approach measures the impact force response signals generated by multiple impacts occurring during the rebound process following the initial impact. These signals are converted into a cumulative energy-based indicator, which is then used for strength evaluation. To implement this approach, a dedicated experimental system capable of impact generation and signal measurement was newly designed and assembled. An initial impact was applied to the specimen using a rotational free-fall mechanism, allowing successive rebound-induced impacts to occur continuously. Concrete specimens with different strength levels and sizes were prepared as test samples, and impact force experiments were conducted to record the response signals generated during the impact process. Based on the measured signals from both the initial and rebound impacts, the total impact force signal energy was calculated for each specimen and compared with the corresponding compressive strength obtained from direct compression tests. The results demonstrated a clear correlation between the total impact force signal energy derived from the response signals and the directly measured compressive strength of the concrete specimens. These findings indicate that the compressive strength of materials, including concrete, can be non-destructively evaluated using the total impact force signal energy obtained from impact force response signals.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 암석 및 콘크리트와 같은 재료의 압축강도를 비파괴적으로 평가하기 위한 방법을 제안하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 단일 타격에 국한하지 않고, 초기 타격 이후 반발 과정에서 발생하는 다중 타격에 따른 타격력 응답신호를 측정하고, 해당 신호를 누적 에너지 지표로 환산하여 강도 평가에 활용하였다. 연구 수행을 위하여 타격 및 신호 계측이 가능한 실험 장치를 새롭게 설계·구성하였으며, 회전 자유낙하 방식으로 시험체에 초기타격을 가하고 반발에 의한 반복 타격이 연속적으로 발생하도록 하였다. 시험 대상은 서로 다른 강도와 크기를 갖는 콘크리트 시편으로 선정하였고, 각 시편에 대해 타격력 실험을 수행하여 타격 과정에서 발생하는 응답신호를 측정하였다. 측정된 초기 타격 및 반발 타격 신호를 기반으로 시편별 전체 타격력 신호에너지를 산정하였으며, 이를 동일 시편에 대해 측정한 직접 압축강도 결과와 비교·분석하였다. 그 결과, 타격력 응답신호로부터 도출된 전체 타격력 신호에너지는 콘크리트 시편의 직접 압축강도와 뚜렷한 상관관계를 보이는 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 결과를 통해, 콘크리트를 포함한 재료의 압축강도는 타격 과정에서 획득한 타격력 응답신호를 이용하여 비파괴적으로 평가할 수 있음을 확인하였다.
-
A Study on the Nondestructive Method for Estimating the Compressive Strength of Materials
-
-
Relationship Between Wall Displacement and Safety Factor of Temporary Earth Retaining Structures Through Numerical Analysis
수치해석을 통한 가설 흙막이 벽체의 변위-안전율 관계
-
Yeonoh Moon, Seongwo Lee, Hyuksang Jung
문연오, 이성우, 정혁상
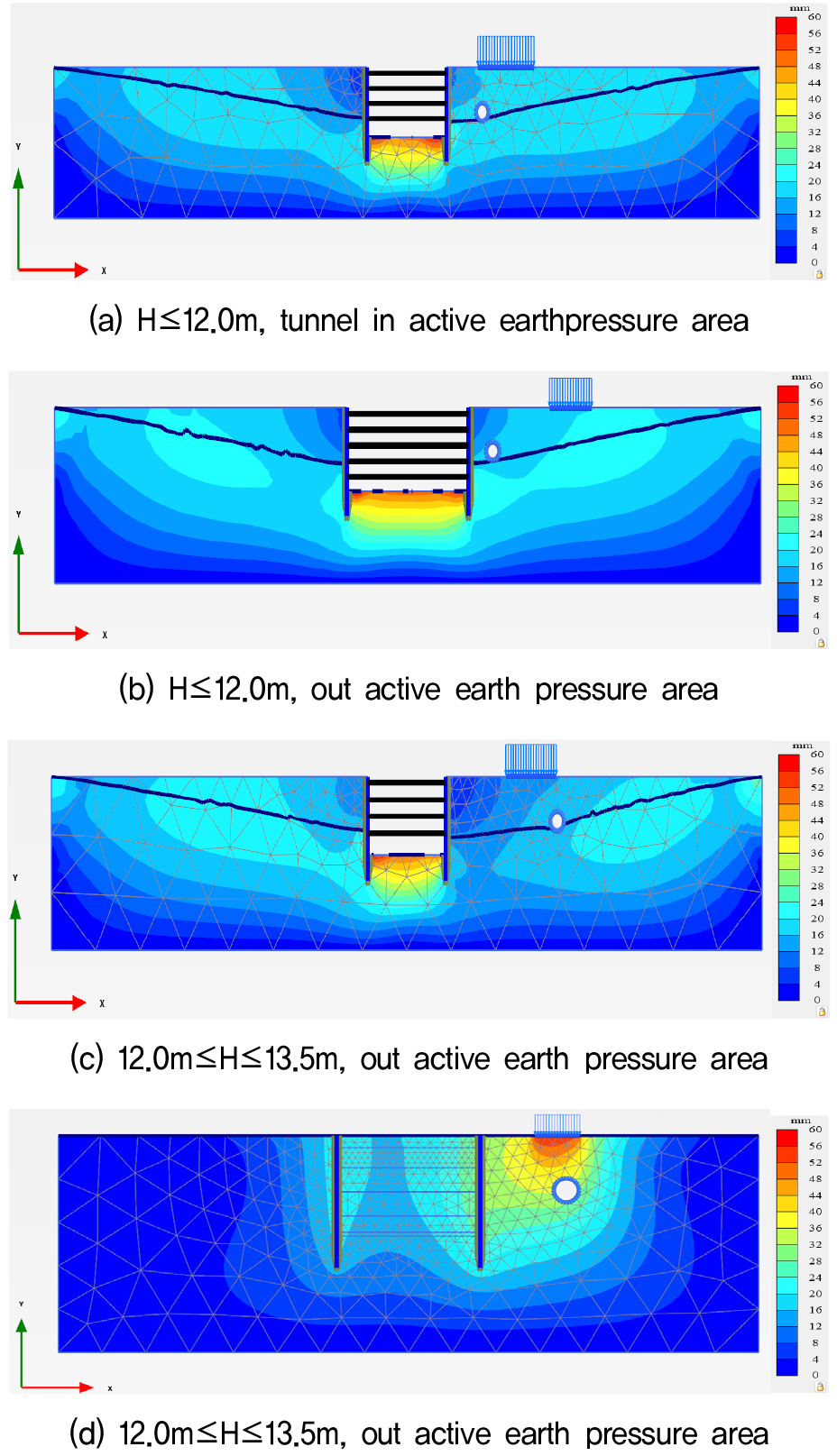
- This study investigates the relationship between wall displacement and the factor of safety of temporary retaining walls through numerical analysis. Numerical analyses …
본 연구에서는 수치해석을 통해 가설 흙막이 벽체에서 발생하는 변위와 안전율의 관계를 분석한다. 2차원 평면변형률 조건에서 지반조건, 인접기초 이격거리, 기초의 크기, 하중 등의 …
- This study investigates the relationship between wall displacement and the factor of safety of temporary retaining walls through numerical analysis. Numerical analyses were performed considering various conditions, including ground conditions, separation distance from adjacent foundations, foundation size, and applied loads. The analyses assumed a situation in which the retaining wall is installed in adjacent ground where foundations and tunnels have already been constructed. The results indicate that wall displacement is strongly influenced by geometric conditions, while the factor of safety is mainly affected by factors related to the mobilization of resistance and sliding of the retained ground. In addition, when the wall displacement satisfied the design criteria, the factor of safety was also found to meet the required standards. However, when the displacement exceeded the allowable limits, the reliability of the factor of safety was significantly reduced.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 수치해석을 통해 가설 흙막이 벽체에서 발생하는 변위와 안전율의 관계를 분석한다. 2차원 평면변형률 조건에서 지반조건, 인접기초 이격거리, 기초의 크기, 하중 등의 다양한 조건을 고려하여 수치해석을 수행하며, 기초 및 터널이 시공완료된 인접 지반에 벽체가 설치되는 경우를 가정하여 연구를 수행한다. 연구 결과 벽체의 변위는 기하학 조건들에 영향을 많이 받으며, 안전율의 경우 배면지반의 활동과 저항에 관여하는 인자들이 영향을 미치는 것을 알 수 있었다. 또한, 벽체의 변위가 설계기준에 만족하는 경우 안전율 또한 만족하였지만, 기준치를 초과하는 변위가 발생된 경우 안전율에 대한 신뢰도가 매우 떨어지는 것으로 나타났다.
-
Relationship Between Wall Displacement and Safety Factor of Temporary Earth Retaining Structures Through Numerical Analysis
-
-
Applicability of Simplified Liquefaction Assessment Methods Examined Using Effective-Stress Analysis
유효응력해석을 활용한 액상화 간편예측법의 적용성 분석
-
Sunwo Hyun, Seokho Jeong
현선우, 정석호
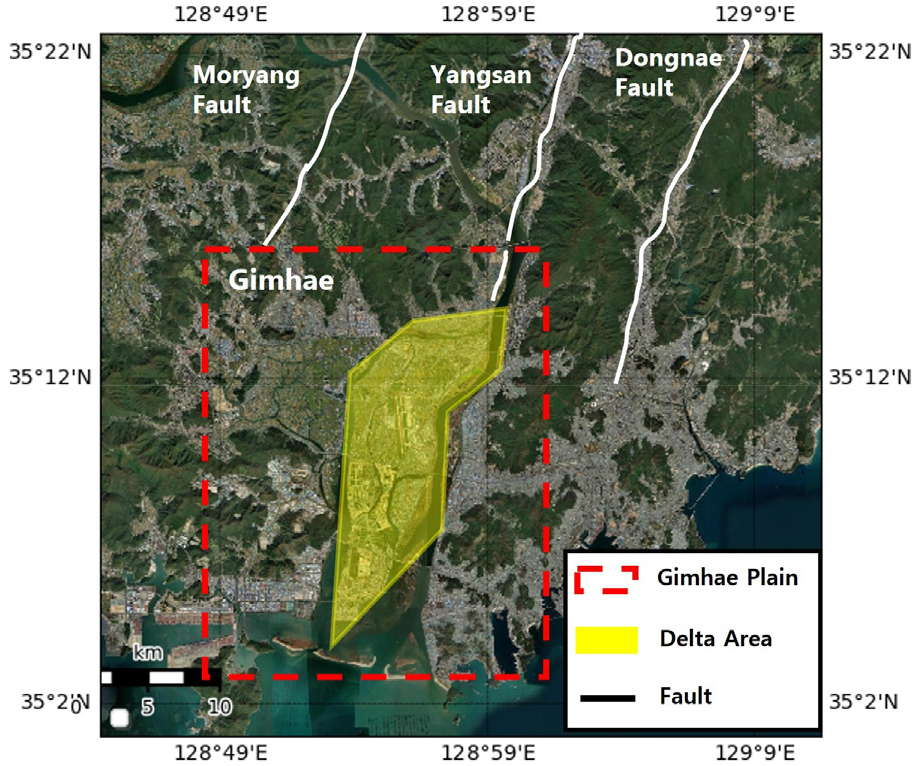
- Liquefaction induced ground failures observed during the 2017 Pohang earthquake have raised concerns about liquefaction hazard in Korea. However, the widely used …
2017년 포항지진에서 액상화가 관측되면서 국내 지반 안정성에 대한 우려가 커졌다. 그러나 실무에서 널리 사용되는 액상화 평가 간편법은 경험적 상관관계에 기반하므로, 국내 지반 …
- Liquefaction induced ground failures observed during the 2017 Pohang earthquake have raised concerns about liquefaction hazard in Korea. However, the widely used simplified liquefaction evaluation method relies on empirical correlations, necessitating validation for domestic soil conditions. This study compares the simplified method with effective stress analysis in the Nakdong River Delta, assuming a Mw 6.2 scenario earthquake on the Dongnae Fault. Effective stress analysis was performed using the PDMY02 model in OpenSeesPy, incorporating dynamic properties derived directly from cyclic triaxial tests on Nakdong River sand. The results indicate that the simplified method tends to overestimate or underestimate risk by failing to account for the progressive accumulation of excess pore water pressure. Furthermore, analysis using lab-calibrated parameters predicted more localized liquefaction zones. In contrast, models using the OpenSees Wiki reference parameter set tended to overestimate liquefaction potential. These findings suggest that accurate liquefaction assessment in Korea requires effective stress analysis incorporating site-specific laboratory data.
- COLLAPSE
2017년 포항지진에서 액상화가 관측되면서 국내 지반 안정성에 대한 우려가 커졌다. 그러나 실무에서 널리 사용되는 액상화 평가 간편법은 경험적 상관관계에 기반하므로, 국내 지반 조건에 대한 적용성 분석이 필요하다. 본 연구는 낙동강 삼각주 지역의 대표 지점을 선정하여 유효응력 해석법을 활용한 액상화 평가를 실시하고, 그 결과를 현행 간편법과 비교·분석하였다. 액상화 평가를 위해 동래단층 상에 규모 6.2의 가상 지진 시나리오를 가정하고, 광대역 하이브리드 지반운동 시뮬레이션을 통해 입력 지반운동을 생성하였다. 유효응력 해석은 OpenSeesPy의 PDMY02 재료모델을 활용하였으며, 특히 낙동강사에 대한 반복삼축압축 시험을 직접 수행하여 산정된 동적 물성치를 해석에 반영하였다. 연구 결과, 간편법은 지진 지속시간 동안의 과잉간극수압 축적 양상을 고려하지 못해 유효응력 해석 대비 위험도를 과대 또는 과소평가하는 경향이 나타났다. 또한, 실내 실험 값을 반영한 유효응력 해석은 문헌값을 적용했을 때보다 액상화 발생 범위를 더 국부적으로 예측하였으며, 문헌값 적용 결과가 액상화 위험도를 다소 과대평가하는 경향이 있음을 확인하였다. 본 연구 결과는 국내 지반 조건에 적합한 액상화 평가를 위해서는 간편법에만 의존하기보다, 현장 시료를 이용한 실내 실험을 통해 지반의 동적 특성을 파악하고 이를 반영한 유효응력 해석을 병행할 필요가 있음을 시사한다.
-
Applicability of Simplified Liquefaction Assessment Methods Examined Using Effective-Stress Analysis
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society








