-
-
Urban Seismic Risk Assessment Integrating Site Classification-Based Geotechnical Hazard, Exposure, and Vulnerability: A GIS-MCDA Approach
부지분류 기반 지반 재해 인자와 노출·취약성 요인을 통합한 서울시 지진 위험도 평가: GIS-MCDA 접근법
-
Jihye Kim, Jinkwon Yoo, Youngkarb Song, Youngsuk Lee
김지혜, 유진권, 송영갑, 이영석
- This study proposes a high-resolution seismic risk assessment framework for Seoul to support an enhanced understanding of urban seismic risk patterns. The …
본 연구는 서울의 지진 위험 특성을 보다 정밀하게 진단하기 위해, 지반공학적 요인과 도시 공간의 사회적 요인을 통합한 고해상도 지진 위험도 평가 체계를 …
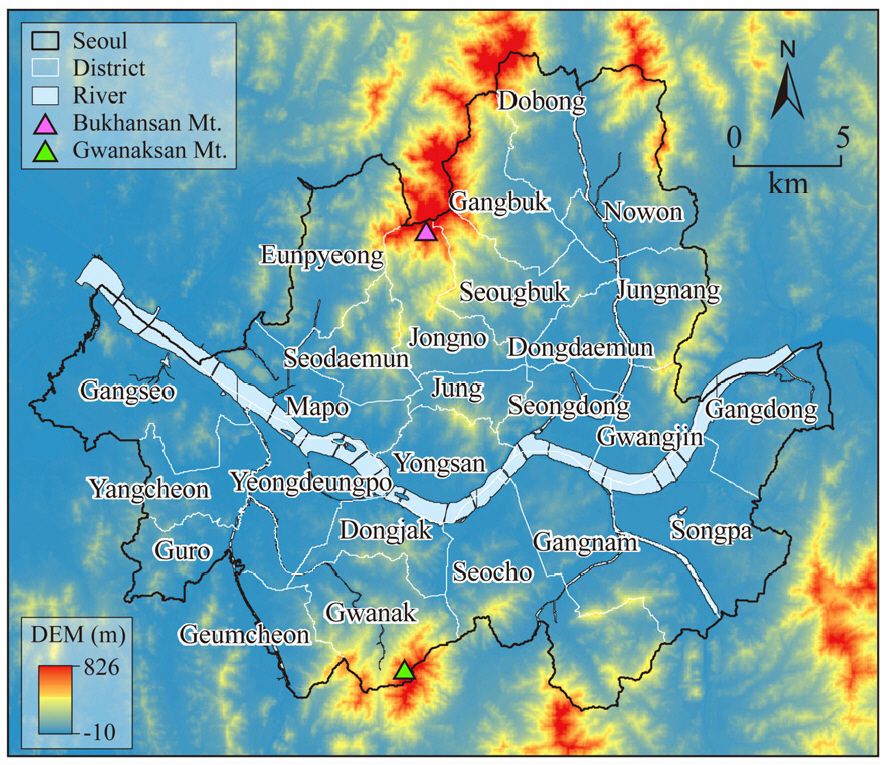
- This study proposes a high-resolution seismic risk assessment framework for Seoul to support an enhanced understanding of urban seismic risk patterns. The framework evaluates seismic risk at a 250 m grid scale to capture spatial heterogeneity within the city. The assessment integrates Hazard (site-specific amplification potential), Exposure (quantitative concentration of assets and populations), and Vulnerability (sensitivity of physical and demographic components) using a GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) approach. The results indicate that seismic risk in Seoul tends to be locally concentrated in areas where multiple risk components spatially overlap. High-risk hotspots requiring priority attention accounted for approximately 0.3% of the total study area. The dominant contribution to overall risk levels was associated with Exposure–Vulnerability interactions, suggesting that the concentration of vulnerable assets and populations rather than ground conditions. Furthermore, high-risk zones were classified into three typological categories based on their prevailing risk characteristics. These findings provide implications for region-specific risk management strategies, including seismic retrofitting and targeted support for vulnerable populations, to inform urban resilience planning.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 서울의 지진 위험 특성을 보다 정밀하게 진단하기 위해, 지반공학적 요인과 도시 공간의 사회적 요인을 통합한 고해상도 지진 위험도 평가 체계를 제시하였다. 국제적 재난 리스크 평가 체계에 기반하여 재해 인자, 노출, 취약성으로 구성된 위험 요소를 설정하고, 이를 GIS 기반 다기준 의사결정 분석(MCDA)을 통해 통합적으로 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 서울시의 지진 위험도는 위험 요인이 중첩되는 특정 공간에서 국지적으로 집중되는 경향을 보였으며, 즉각적인 관리가 요구되는 고위험 핫스팟은 전체 면적의 약 0.3%로 나타났다. 위험도 수준은 지반 조건보다 자산과 인구의 밀집도 및 취약성이 결합된 특성에 의해 좌우되는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 고위험 지역은 위험 구성 특성에 따라 재해 인자–노출 집중형, 도심 복합 취약형, 주거 밀집 및 인구 취약형의 세 가지 유형으로 분류되었다. 이러한 결과는 내진 성능 보강과 취약계층 보호를 포함한 지역 특성 기반의 도시 회복탄력성 강화 전략을 검토하는 데 기초 자료로 활용될 것으로 기대된다.
-
Urban Seismic Risk Assessment Integrating Site Classification-Based Geotechnical Hazard, Exposure, and Vulnerability: A GIS-MCDA Approach
-
-
Correlation Analysis of Variations in Soft-Ground Soil Parameters in the Namak Area Near Mokpo
목포인근 남악지역의 연약지반 토질상수변화와 상관관계
-
Byeonghun Go, Sangyong Kim, Yongchai Chang
고병훈, 김상용, 장용채
- This study aimed to quantify the correlations among the natural water content (wn), compression index (Cc), coefficient of …
본 연구는 목포인근 남악지역 연약지반을 대상으로 함수비(wn), 압축지수(Cc), 압밀계수(Cv)와 더치콘 관입시험(DCPT) 선단저항(qc) 간의 …
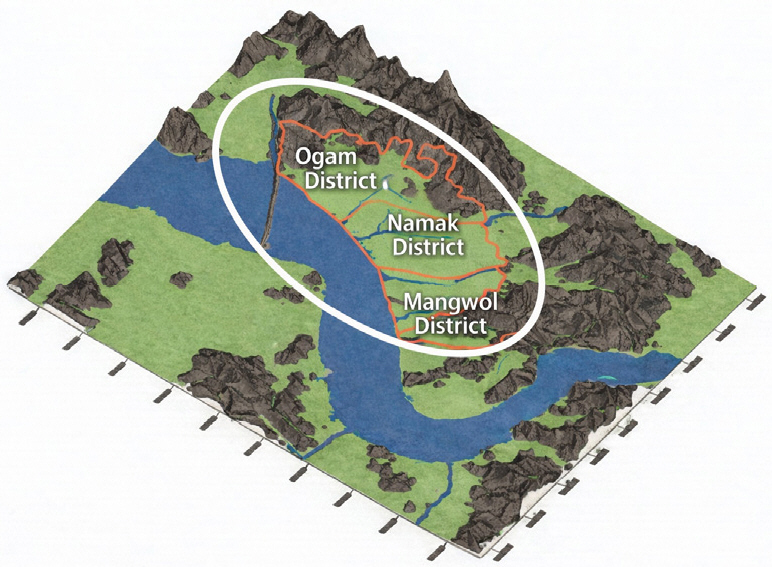
- This study aimed to quantify the correlations among the natural water content (wn), compression index (Cc), coefficient of consolidation (Cv), and cone tip resistance (qc) obtained from the dutch cone penetration test (DCPT) for soft ground in the Namak area near Mokpo and to propose practical empirical equations for engineering applications. A database was established by integrating laboratory test results from borehole sampling (water content and oedometer consolidation tests) with DCPT results measured at the same locations. The analysis was conducted by stratifying the data according to depth intervals, and regression suitability was examined through outlier removal and variable transformations. These equations can be used to reasonably estimate input parameters for consolidation and settlement analyses from DCPT data when laboratory testing is limited during the preliminary design stage.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 목포인근 남악지역 연약지반을 대상으로 함수비(wn), 압축지수(Cc), 압밀계수(Cv)와 더치콘 관입시험(DCPT) 선단저항(qc) 간의 상관관계를 정량화하고, 실무 적용이 가능한 경험식을 제안하는 것을 목적으로 하였다. 대상 지반은 시추·채취시료 기반의 실내시험(함수비, 압밀시험) 결과와 동일 지점 DCPT 결과를 연계하여 데이터베이스를 구축하였다. 분석은 심도구간을 고려하여 층별로 수행하였으며, 이상치 제거 및 변수 변환을 통해 회귀 적합성을 검토하였다. 본 경험식은 초기 설계 단계에서 실내시험이 제한된 경우, DCPT 자료를 기반으로 압밀·침하 해석 입력정수의 합리적 추정에 활용될 수 있다.
-
Correlation Analysis of Variations in Soft-Ground Soil Parameters in the Namak Area Near Mokpo
-
-
Analysis of Pile and Stress Behavior According to Pile Shape in Sand Ground
사질토 지반에서의 말뚝 형상에 따른 말뚝 및 응력 거동 분석
-
Yushin Kim, Seungjun Yang, Yongchai Chang
김유신, 양승준, 장용채
- In sandy ground, pile geometry and the relative density of the soil are key factors governing load transfer characteristics acting on the …
사질토 지반에서 말뚝 관입 시 말뚝 형상과 지반의 상대밀도는 말뚝에 작용하는 하중 전달 특성과 지반 내부 토압 거동을 지배하는 핵심 인자이다. 말뚝 …
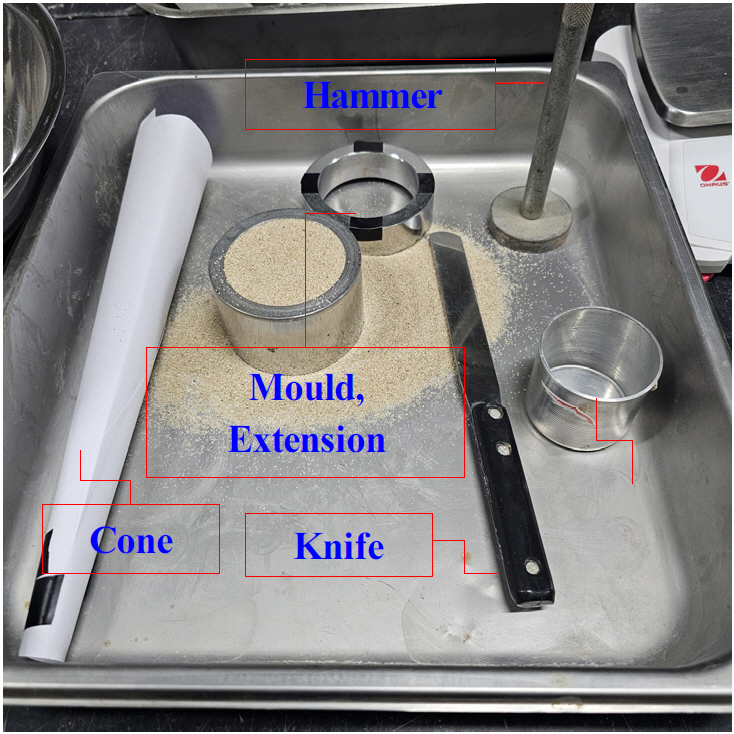
- In sandy ground, pile geometry and the relative density of the soil are key factors governing load transfer characteristics acting on the pile and the associated earth pressure behavior within the ground during pile installation. Most previous studies on pile foundations have primarily focused on the evaluation of ultimate bearing capacity and load–settlement relationships to meet practical design requirements, while relatively limited attention has been paid to the direct investigation of stress evolution in the ground and load transfer mechanisms during pile penetration, as has been pointed out in earlier research, In this study, the relationship between earth pressure measured in the ground and the load applied to the pile during pile penetration is investigated through two-dimensional model tests conducted in a calibration chamber. Two pile geometries are considered: a basic straight pile and a helical pile. The relative density of the sandy ground is set to 40% and 80%, resulting in four test cases in total. By comparing and analyzing the experimental responses of the basic pile and the helical pile, this study aims to identify characteristic trends in load transfer and earth pressure behavior and to provide practical insights for pile type selection in sandy ground conditions.
- COLLAPSE
사질토 지반에서 말뚝 관입 시 말뚝 형상과 지반의 상대밀도는 말뚝에 작용하는 하중 전달 특성과 지반 내부 토압 거동을 지배하는 핵심 인자이다. 말뚝 관련 연구는 극한지지력 산정과 하중 – 침하(load–settlement) 관계 분석이 실무에 맞춰 수행되는 것이 일반적이고, 말뚝 관입 과정에서 발생하는 지반 내부 응력 변화와 하중 전달 메커니즘을 직접적으로 분석한 연구는 상대적으로 제한적이다. 본 연구는 모의 토조에서 2차원 말뚝 관입 과정을 통해 측정된 토압과 말뚝에 가해지는 하중의 상관관계를 해석한다. 말뚝의 형상은 Basic Pile, Helical Pile로 분류하며, 상대밀도는 40%, 80%로 설정하여 4가지 경우를 분석하였다. 연구를 통해 최종적으로 Basic Pile과 Helical Pile의 실험 결과에 경향을 분석하여 사질토 지반의 말뚝 선정에 대하여 참고할 수 있는 기준을 제시하려고 한다.
-
Analysis of Pile and Stress Behavior According to Pile Shape in Sand Ground
-
-
Fuel Characteristics of a Non-Woody Biomass Solid Fuel Produced from Coffee Grounds and Inorganic Additives
커피박과 무기성 자원을 활용한 비목재계 바이오매스 고체연료의 연료 특성 평가
-
Wonseok Seo, Jungkwon Kim
서원석, 김정권
- This study investigated the fuel performance and combustion residue characteristics of a non-woody biomass solid fuel using spent coffee grounds as the …
본 논문은 커피박을 주된 유기 연료원으로 활용하고 조개껍질 유래 CaCO3 및 태백 경석을 무기 첨가제로 적용한 비목질계 바이오매스 고형연료의 연료 성능과 …
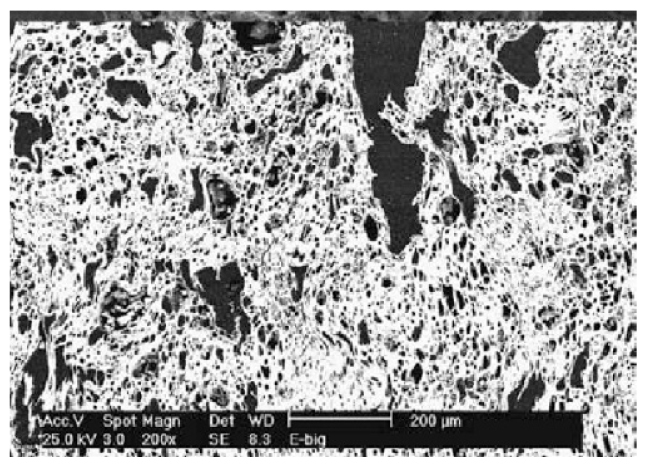
- This study investigated the fuel performance and combustion residue characteristics of a non-woody biomass solid fuel using spent coffee grounds as the primary organic fuel source, with seashell-derived CaCO3 and Taebaek pumice applied as inorganic additives. The solid fuel was produced through a low-temperature torrefaction process, followed by high-pressure molding and hydrocarbon-based surface coating, and its fuel quality was evaluated in accordance with the EN ISO 17225-6 standard. Under optimized conditions, the produced fuel satisfied key quality requirements, including heating value, moisture content, ash content, and fixed carbon content, and exhibited compressive strength exceeding 10 MPa, ensuring adequate mechanical stability for handling and transportation. In addition, water resistance was improved by approximately 20% compared to conventional coffee-ground pellets, while statistical analysis confirmed that torrefaction temperature and CaCO3 content have a significant effect on fuel performance. Furthermore, combustion residue analysis verified the conversion of CaCO3 to CaO, suggesting the potential recyclability of the combustion residues.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문은 커피박을 주된 유기 연료원으로 활용하고 조개껍질 유래 CaCO3 및 태백 경석을 무기 첨가제로 적용한 비목질계 바이오매스 고형연료의 연료 성능과 연소 잔재 특성을 규명하였다. 저온 토리파이드 공정과 고압 성형, 탄화수소계 표면 코팅을 통해 고형연료를 제조하였으며, 연료 품질 평가는 EN ISO 17225-6 기준에 따라 수행되었다. 그 결과 최적 조건에서 제조된 연료는 발열량, 수분·회분 함량, 고정탄소 함량 등 주요 품질 지표에서 기준을 충족하였고, 압축강도 10MPa 이상으로 취급 및 운송에 적합한 기계적 안정성을 확보하였다. 또한 내수성은 기존 커피박 펠릿 대비 약 20% 향상되었으며, 통계 분석 결과 토리파이드 온도와 CaCO3 함량이 연료 성능에 유의미한 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다. 더불어 연소 잔재 분석을 통해 CaCO3의 CaO 전환이 확인되어 잔재의 재활용 가능성이 제시되었다.
-
Fuel Characteristics of a Non-Woody Biomass Solid Fuel Produced from Coffee Grounds and Inorganic Additives
-
-
A Case Study on the Performance Analysis of Upper Slope Reinforcement Members during Blasting Excavation at a Tunnel Portal
터널갱구부 발파굴착 시 상부 비탈면 보강 부재 성능 분석 사례 연구
-
Jongki Lee
이종기
- Slope reinforcement structures constructed in rock masses may experience degradation in structural performance when subjected to external dynamic loads such as earthquakes …
비탈면 보강시설물은 암반층에 시공되지만, 시공 이후 지진이나 발파와 같은 외부 충격이 작용할 경우 구조적 성능이 저하되어 시설물의 안정성과 사용수명에 영향을 받을 수 …
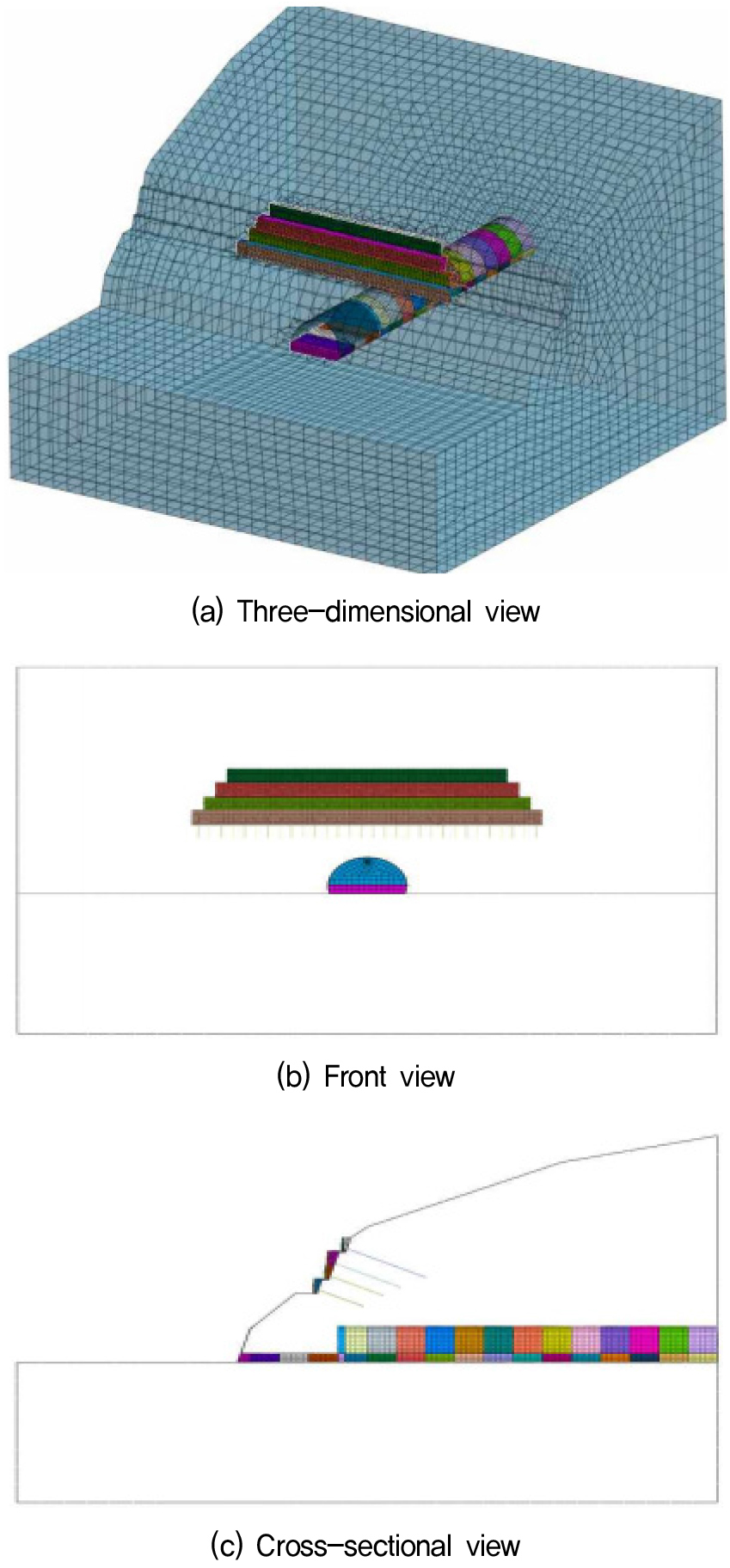
- Slope reinforcement structures constructed in rock masses may experience degradation in structural performance when subjected to external dynamic loads such as earthquakes or blasting after installation, which can adversely affect their stability and service life. In particular, reinforcement systems applied at tunnel portal slopes, including panel-type retaining walls and ground anchors, form integrated rock–structure systems through steel tendons and cement grout, making them susceptible to blasting-induced vibrations. Nevertheless, current blasting design practices primarily focus on preventing damage to nearby surface facilities and do not sufficiently consider potential damage to slope reinforcement structures located within the blasting influence zone.In this study, the damage characteristics of rock-integrated reinforcement systems—including panel-type retaining walls, anchor-supported composite structures, and soil nails—installed at tunnel portal slopes were evaluated under nearby blasting conditions. In addition, the effects of post-construction condition changes, such as tunnel excavation, on long-term performance were analyzed to provide fundamental data for improving future design and management criteria.
- COLLAPSE
비탈면 보강시설물은 암반층에 시공되지만, 시공 이후 지진이나 발파와 같은 외부 충격이 작용할 경우 구조적 성능이 저하되어 시설물의 안정성과 사용수명에 영향을 받을 수 있다. 특히 터널 갱구부 비탈면에 적용되는 패널식 옹벽, 어스앵커 등의 보강공법은 강연선과 시멘트 그라우트를 통해 암반과 일체화된 구조로 형성되어 발파진동에 의한 손상 가능성을 내재하고 있다. 그럼에도 불구하고 현행 발파설계는 인접 일반 시설물의 손상 방지에 중점을 두고 있어, 발파 영향범위 내 비탈면 보강시설물의 손상은 충분히 고려되지 못하고 있다.이에 본 연구에서는 터널 갱구부 비탈면에 적용되는 패널식 옹벽, 앵커 결합구조물, 소일네일 등 암반 일체화형 보강시설물을 대상으로 근접 발파에 따른 손상 특성을 평가하고, 터널 굴착 등 시공 이후 조건 변화가 장기 성능에 미치는 영향을 분석하여 향후 설계 및 관리 기준 마련을 위한 기초자료를 제시하고자 하였다.
-
A Case Study on the Performance Analysis of Upper Slope Reinforcement Members during Blasting Excavation at a Tunnel Portal
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society
Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society








